Results 1 to 1 of 1
Thread Information
Users Browsing this Thread
There are currently 1 users browsing this thread. (0 members and 1 guests)
Hybrid View
-
08-11-2008, 08:06 PM #1Senior Member


- Join Date
- May 2007
- Location
- South West Florida (Behind friendly lines but still in Occupied Territory)
- Posts
- 117,696
War in the Caucasus: Towards a Broader Russia-US Military Co
War in the Caucasus: Towards a Broader Russia-US Military Confrontation?
by Michel Chossudovsky
Global Research, August 10, 2008

During the night of August 7, coinciding with the opening ceremony of the Beijing Olympics, Georgia's president Saakashvili ordered an all-out military attack on Tskhinvali, the capital of South Ossetia.
The aerial bombardments and ground attacks were largely directed against civilian targets including residential areas, hospitals and the university. The provincial capital Tskhinvali was destroyed. The attacks resulted in some 1500 civilian deaths, according to both Russian and Western sources. "The air and artillery bombardment left the provincial capital without water, food, electricity and gas. Horrified civilians crawled out of the basements into the streets as fighting eased, looking for supplies." (AP, August 9, 200 . According to reports, some 34,000 people from South Ossetia have fled to Russia. (Deseret Morning News, Salt Lake City, August 10, 200
. According to reports, some 34,000 people from South Ossetia have fled to Russia. (Deseret Morning News, Salt Lake City, August 10, 200
The importance and timing of this military operation must be carefully analyzed. It has far-reaching implications.
Georgia is an outpost of US and NATO forces, on the immediate border of the Russian Federation and within proximity of the Middle East Central Asian war theater. South Ossetia is also at the crossroads of strategic oil and gas pipeline routes.
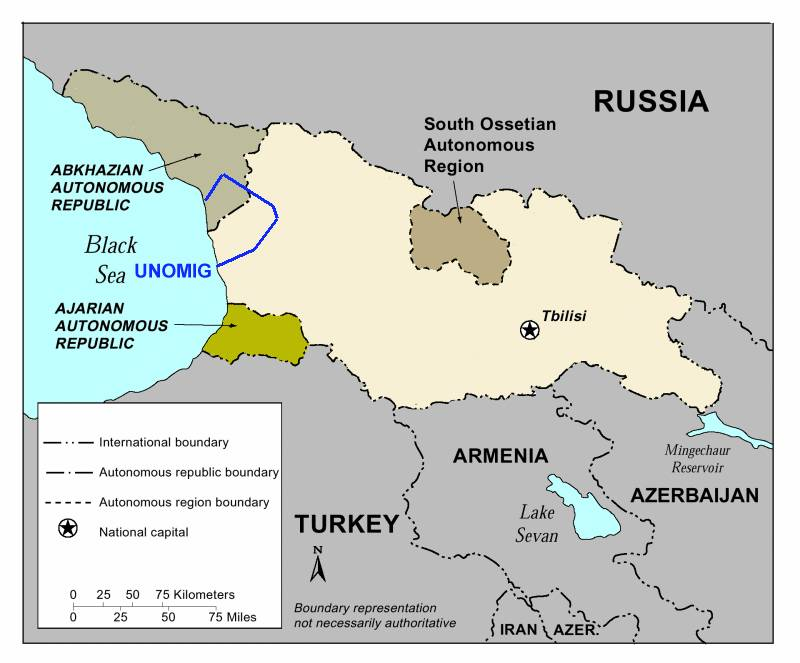
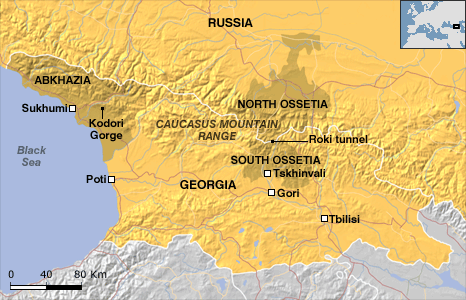
Georgia does not act militarily without the assent of Washington. The Georgian head of State is a US proxy and Georgia is a de facto US protectorate.
Who is behind this military agenda? What interests are being served? What is the purpose of the military operation.
There is evidence that the attacks were carefully coordinated by the US military and NATO.
Moscow has accused NATO of "encouraging Georgia". Russiaâs Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov underscored the destabilizing impacts of "foreign" military aid to Georgia: .
âIt all confirms our numerous warnings addressed to the international community that it is necessary to pay attention to massive arms purchasing by Georgia during several years. Now we see how these arms and Georgian special troops who had been trained by foreign specialists are used,âJoin our efforts to Secure America's Borders and End Illegal Immigration by Joining ALIPAC's E-Mail Alerts network (CLICK HERE)


 LinkBack URL
LinkBack URL About LinkBacks
About LinkBacks






 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote

DHS says 'privacy' of migrants on terrorist watchlist is greater...
05-17-2024, 09:42 PM in illegal immigration News Stories & Reports